- 欢迎来到北京优尼康生物科技有限公司
- |
-
商品分类
 010-64814275
010-64814275

 010-64814275
010-64814275

NF-κB-SEAP & IRF-Lucia reporter liver carcinoma cells
The human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2 is widely used for in vitro studies of infection with hepatitis viruses (except HBV & HCV) and other hepatotropic pathogens such as Human Cytomegalovirus, Dengue Virus, Brucella and Listeria [1, 2].
HepG2-Dual™ cells are designed for the study of NF-κB and IRF (interferon regulatory factor) pathways. NF-κB activation can be assessed by measuring secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) activity, while the IRF pathway can be monitored by following Lucia luciferase activity.
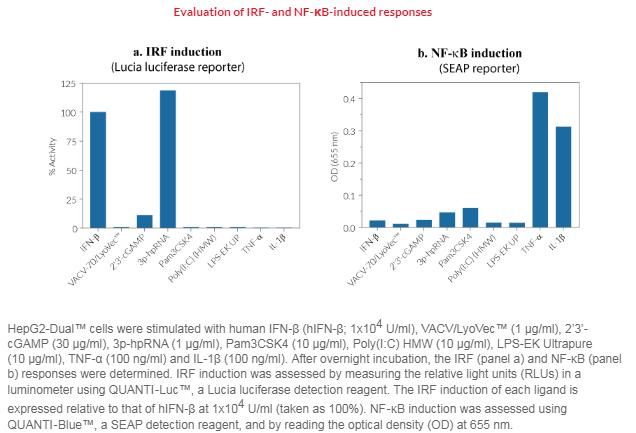
Anti-viral and anti-bacterial immune responses mostly rely on recognition of viral nucleic acids by cytosolic Toll-like receptors (TLRs), cytosolic RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs), and cytosolic DNA sensors (CDS). The TLR expression and activation profile of HepG2 cells is still poorly characterized, but it is established that HepG2 cells express the RIG-I and MDA-5 RNA sensors [2,3]. Although they do not express the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) cytosolic DNA sensor, these cells express low levels of its adaptor protein, STING (stimulator of interferon genes, also known as MITA) [4]. A moderate IRF response is detected in HepG2-Dual™ cells upon incubation with STING agonists such as 2’3’-cGAMP, while the 3p-hpRNA RIG-I agonist, induces a strong IRF response.
Both SEAP and Lucia luciferase reporter proteins are readily measurable in the cell culture supernatant when using QUANTI-Blue™ and QUANTI-Luc™ respectively.
HepG2-Dual™ cells are resistant to blasticidin and Zeocin™.
References:
1. Gural N. et al. 2017. Engineered livers for infectious diseases. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 5:131-44.
2. Yin X. et al. 2017. Hepatitis E virus persists in the presence of a type III interferon response PLoS Pathog. 13(5):e1006417.
3. Sato S. et al. 2015. The RNA sensor RIG-I dually functions as an innate sensor and direct antiviral factor for hepatitis B virus. Immunity. 42(1):123-32.
4. Dansako H. et al., 2016. The cyclic GMP-AMP synthetase-STING signaling pathway is required for both the innate immune response against HBV and the suppression of HBV assembly. FEBS J. 2283(1):144-56.