- 欢迎来到北京优尼康生物科技有限公司
- |
-
商品分类
 010-64814275
010-64814275

 010-64814275
010-64814275

法国HYPHEN BioMed公司(简称HBM)--欧洲知名血液产品生产商,通过国际ISO9001和ISO13485双项认证,生产的大部分产品均通过欧洲CE认证,为临床诊断提供了可靠的保证.
法国HYPHEN BioMed公司是一家生产血栓止血,凝血纤溶和自身免疫的诊断试剂厂家。其产品包括:血凝试剂,发色底物,ELISA试剂盒,人和动物的纯化酶及纯化蛋白,单克隆和多克隆抗体.应用手工或者自动化的方法,为您的实验室诊断、免疫学研究,提供一系列完整的成套试剂,并广泛应用于生物技术和医产业。
发色底物法检测原理:
首先人工合成可以被待测凝血活酶催化裂解的化合物,且化合物连接上产色物质,在检测过程中产色物质可被解离下来,使被检样品中出现颜色变化,根据颜色变化可推算出被检凝血活酶的活性。产色物质一般选用连接对硝基胺(PNA)。游离的PNA呈黄色,其测定波长选用405nm。在这一波长下,其它物质对光的吸收小于PNA对光吸收的1%。具体检测方法即可采用动态法、也可采用终点法。动态法即是连续记录样品的吸光度变化,算出单位时间吸光度的变化量,并以每分钟吸光度的变化来报告结果。终点法即是指在活性酶同产色物质作用一段时间后,加入乙酸终止反应,检测此段时间内吸光度的变化,进而推算出待检酶的活性。凝血仪上多数采用动态法,因为它比终点法简单、结果更为准确。其优点主要表现在:
用酶学方法直接定量、测定结果准确、重复性好、便于自动化和标准化、所需样品量小。
凝血仪使用产色物质在检测血栓/止血指标时大致可分成三种模式。
①对酶的检测:
即在含酶的样品中直接加入产色物质,因为酶可裂解产色物质释放PNA,监测由于PNA释放而导致被检样品在405nm处光吸收的变化,就可推算样品中酶的活性。如对凝血酶、纤溶酶等的检测。
②对酶原的检测:
要对某种酶原进行测定,必须先用激活剂将其激活,使其活化位点暴露,才可将产色物质上的PNA裂解下来。加入的激活剂必须过量,因为只有这样才能使酶原被全部激活,酶原的量才会同样品中酶的活性成一定的数量关系。样品中酶的活性可通过PNA释放,即样品吸光度的变化反应出来,由此则可推算出样品中酶原的含量。
③对酶抑制物的检测:
首先往待检样品中加入过量对应的酶中和该抑制物,剩余的酶可裂解产色物质释放PNA,监测由于PNA释放而导致光吸收的变化,就可测出酶的活性,进而可推算出样品中抑制物的含量。如对抗凝血酶Ⅲ(AT-Ⅲ)等。
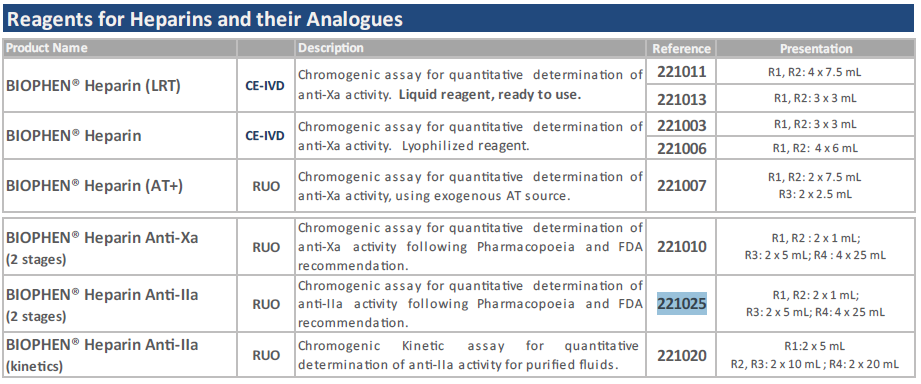
INTENDED USE:
This Heparin Anti-IIa method is a two stage chromogenic assay for measuring the
concentration of heparin, and heparin like anticoagulants, using an automatic or a manual
method, for heparin concentration ranges from 0.002 to 0.04 IU/ml (*) in the tested dilution
(or from 0 to 1 IU/ml in plasma tested diluted 1:25). This method can be used for testing
heparin in human citrated plasma, or in purified solutions.
TEST PRINCIPLE:
The Heparin Anti-IIa method is a two stage chromogenic anti-IIa assay developed for
measuring heparin (UFH), or heparin like anticoagulants, in human citrated plasma, or in
purified solutions, for their Anti-IIa activity.
Heparin is a sulphated polysaccharide with a high affinity for antithrombin. When
complexed with heparin, antithrombin exhibits a fast acting and potent inhibitory activity for
coagulant serine esterases: IXa, Xa and thrombin. LMWH, and heparin analogues, such as
Sodium Danaparoïd, inhibit more efficiently Factor Xa than thrombin, whilst UFH inhibits
efficiently thrombin and also the other serine esterases. Anti-IIa assays are then the right
methods for measuring the anti-thrombin activity of large heparin molecules.
The Heparin Anti-IIa method is a two stage method based on the inhibition of a constant
amount of Thrombin (IIa), by the tested heparin in presence of exogenous antithrombin,
then hydrolysis of a Thrombin specific chromogenic substrate, by Thrombin in excess. pNA
is then released from the substrate. The amount of pNA released is then a relation of the
residual Thrombin activity. There is an inverse relationship between the concentration of
heparin and color development, measured at 405 nm.
Heparin + AT [AT Hep.]
[AT Hep.] + [IIa (excess)] [FIIa-AT-Hep.] + [residual FIIa]
[FIIa (residual)] + IIa-Subs. Peptide + pNA